Python Data Structures
There are different types of data structures available in python which can be broadly categorised into 3 categories:
-
Primary
-
List
-
Dictionary
-
-
Secondary
-
Tuple
-
Set
-
-
Tertiary
-
Stack
-
Queue
-
Deque
-
Heap / Priority Queue
-
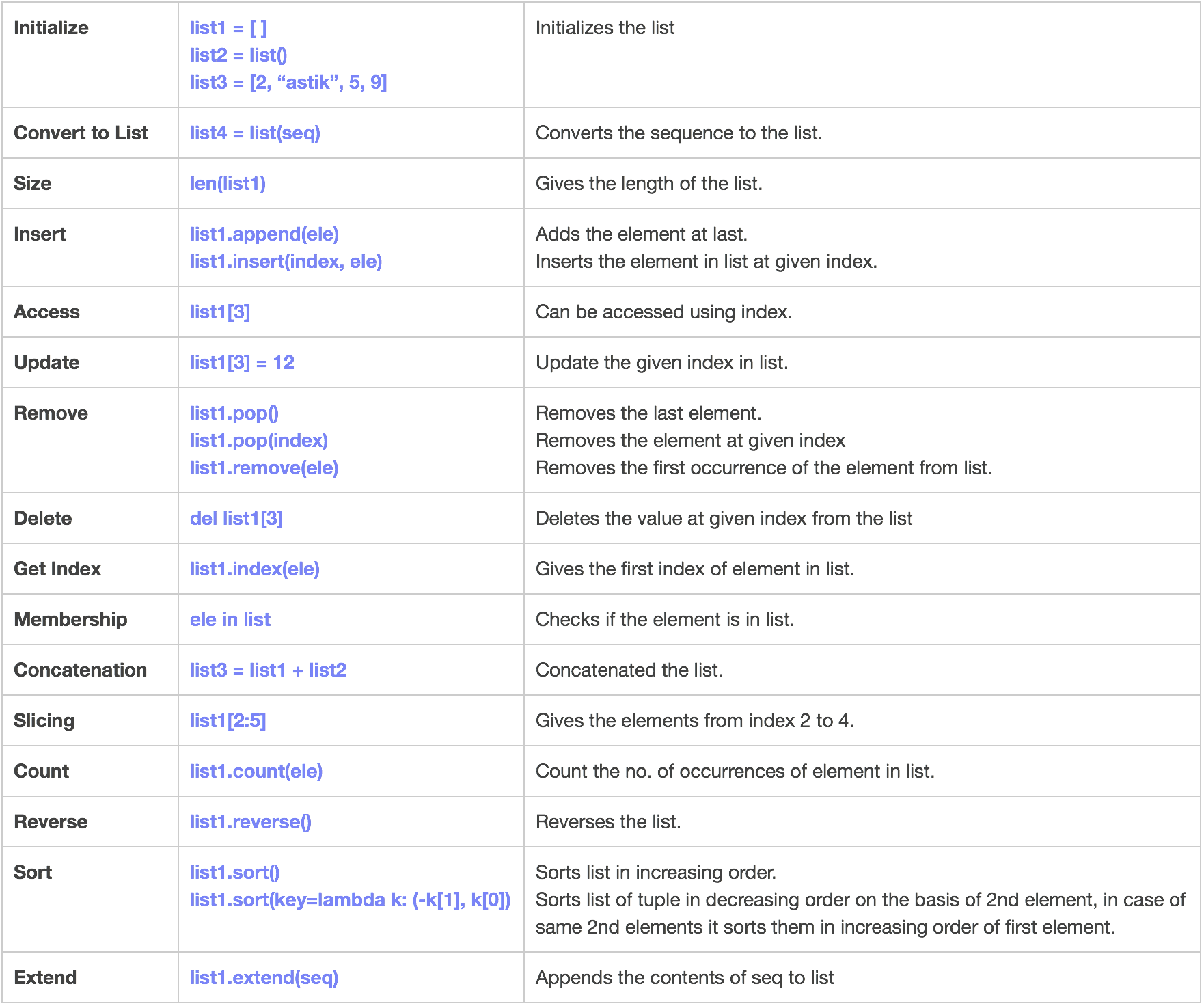
List
Dictionary
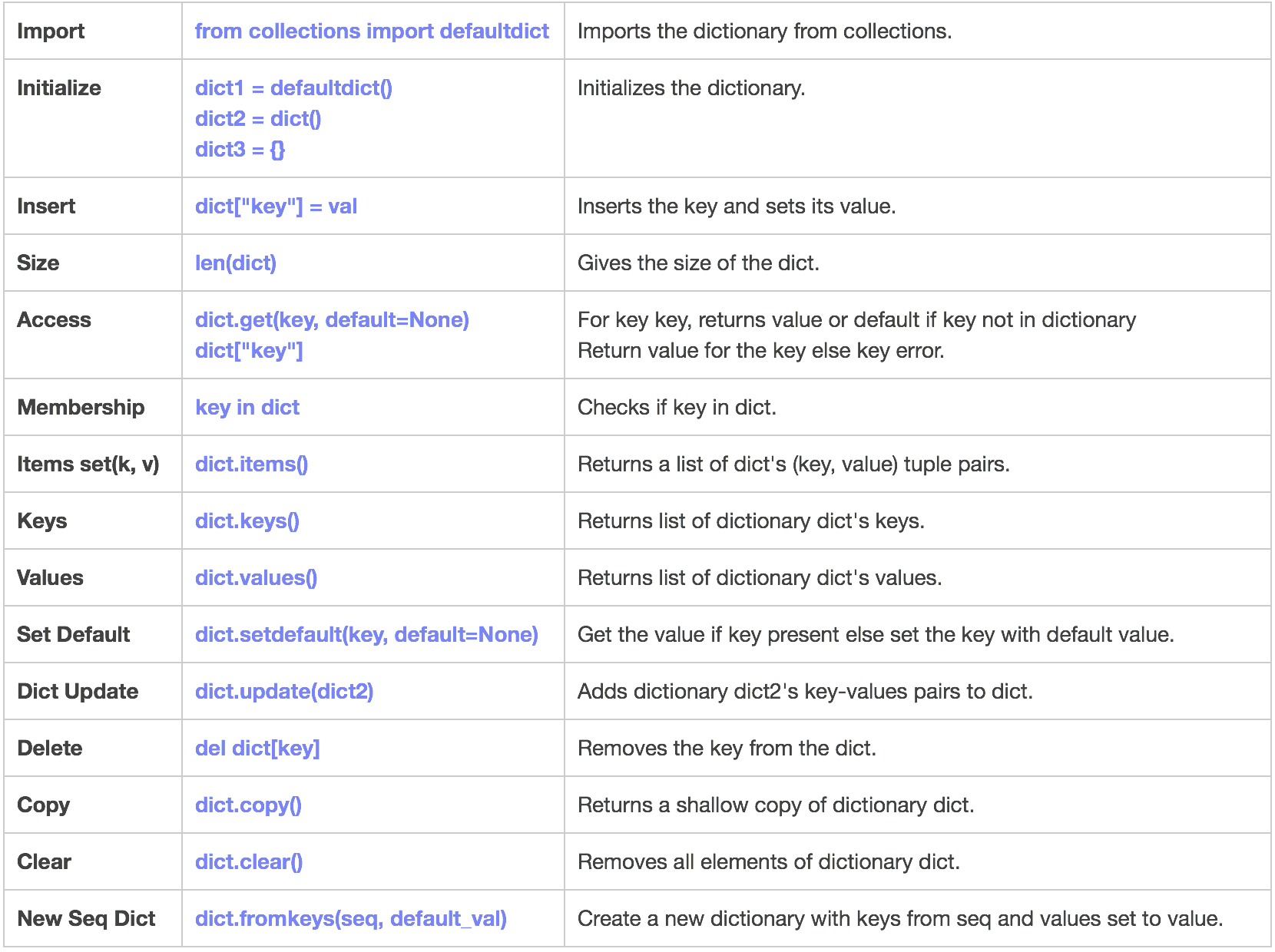
- Dictionary in Python is an unordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map.
- Unlike other Data Types that hold only single value as an element, Dictionary holds key:value pair.
- Key value is provided in the dictionary to make it more optimized.
- Each key-value pair in a Dictionary is separated by a colon :, whereas each key is separated by a ‘comma’.
- A Dictionary in Python works similar to the Dictionary in a real world.
- Keys of a Dictionary must be unique and of immutable data type such as Strings, Integers and tuples, but the key-values can be repeated and be of any type.
Implementation
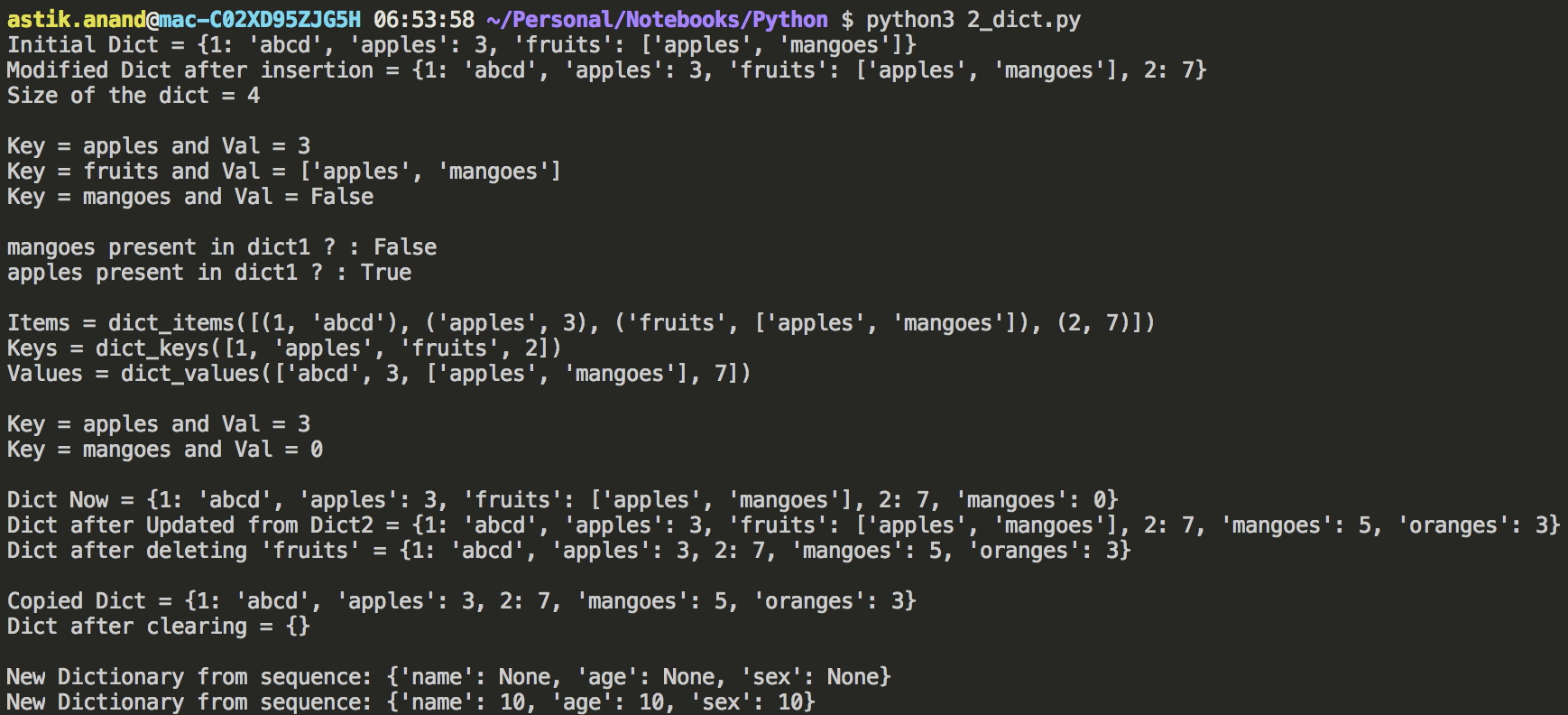
# initialize
dict1 = {1: "abcd", "apples": 3, "fruits": ["apples", "mangoes"], }
print("Initial Dict = {}".format(dict1))
# Insert
dict1[2] = 7
print("Modified Dict after insertion = {}".format(dict1))
# len(): size of the dict
print("Size of the dict = {}\n".format(len(dict1)))
# get(): access
print("Key = {} and Val = {}".format("apples", dict1["apples"]))
print("Key = {} and Val = {}".format("fruits", dict1.get("fruits", False)))
print("Key = {} and Val = {}\n".format("mangoes", dict1.get("mangoes", False)))
# key in dict: Membership check
print("mangoes present in dict1 ? : {}".format("mangoes" in dict1))
print("apples present in dict1 ? : {}\n".format("apples" in dict1))
# items(): set of key, val
print("Items = {}".format(dict1.items()))
# keys(): all the keys of dict
print("Keys = {}".format(dict1.keys()))
# values(): all the values of dict
print("Values = {}\n".format(dict1.values()))
# setdefault(): get the value if key present else sets the default value to key
print("Key = {} and Val = {}".format("apples", dict1.setdefault("apples", 0)))
print("Key = {} and Val = {}\n".format("mangoes", dict1.setdefault("mangoes", 0)))
print("Dict Now = {}".format(dict1))
# update(): update from other dictionary
dict2 = {"mangoes": 5, "oranges": 3}
dict1.update(dict2)
print("Dict after Updated from Dict2 = {}".format(dict1))
# del: delete the key
del dict1["fruits"]
print("Dict after deleting 'fruits' = {}\n".format(dict1))
# copy(): copy the dict
dict2 = dict1.copy()
print("Copied Dict = {}".format(dict2))
# clear(): clear the dict
dict1.clear()
print("Dict after clearing = {}\n".format(dict1))
# fromkeys(): dict from keys
seq = ('name', 'age', 'sex')
print ("New Dictionary from sequence: {}".format(dict.fromkeys(seq)))
print ("New Dictionary from sequence: {}".format(dict.fromkeys(seq, 10)))
Output:
Tuple
- A Tuple is a collection of Python objects separated by commas.
- In someways a tuple is similar to a list in terms of indexing, nested objects and repetition but a tuple is immutable unlike lists which are mutable.

Implementation:
# creation of tuple
tup1 = ('physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000)
# Convert to tuple
tup2 = tuple([2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 6])
# Both tuple initially
print("Tuple tup1 : {}".format(tup1))
print("Tuple tup2 : {}\n".format(tup2))
# access
print("4th Element in tup1 : {}".format(tup1[3]))
print("4th Element in tup2 : {}\n".format(tup2[3]))
# Size of tup1
print("Size of tup1: {}".format(len(tup1)))
# Concatenation
tup3 = tup1 + tup2
print("Concatenated Tuple tup3 : {}\n".format(tup3))
# Membership
print("chemistry present in tup1 ? : {}".format('chemistry' in tup1))
print("chemistry present in tup2 ? : {}\n".format('chemistry' in tup2))
# Max-Min
print("Max of tup2 : {}".format(max(tup2)))
print("Min of tup2 : {}".format(min(tup2)))
# Slicing
print("tup2[2:5] : {}\n".format(tup2[2:5]))
# Delete
del tup1
print("Tuple tup1 after deleting: {}".format(tup1))
Output:

Set
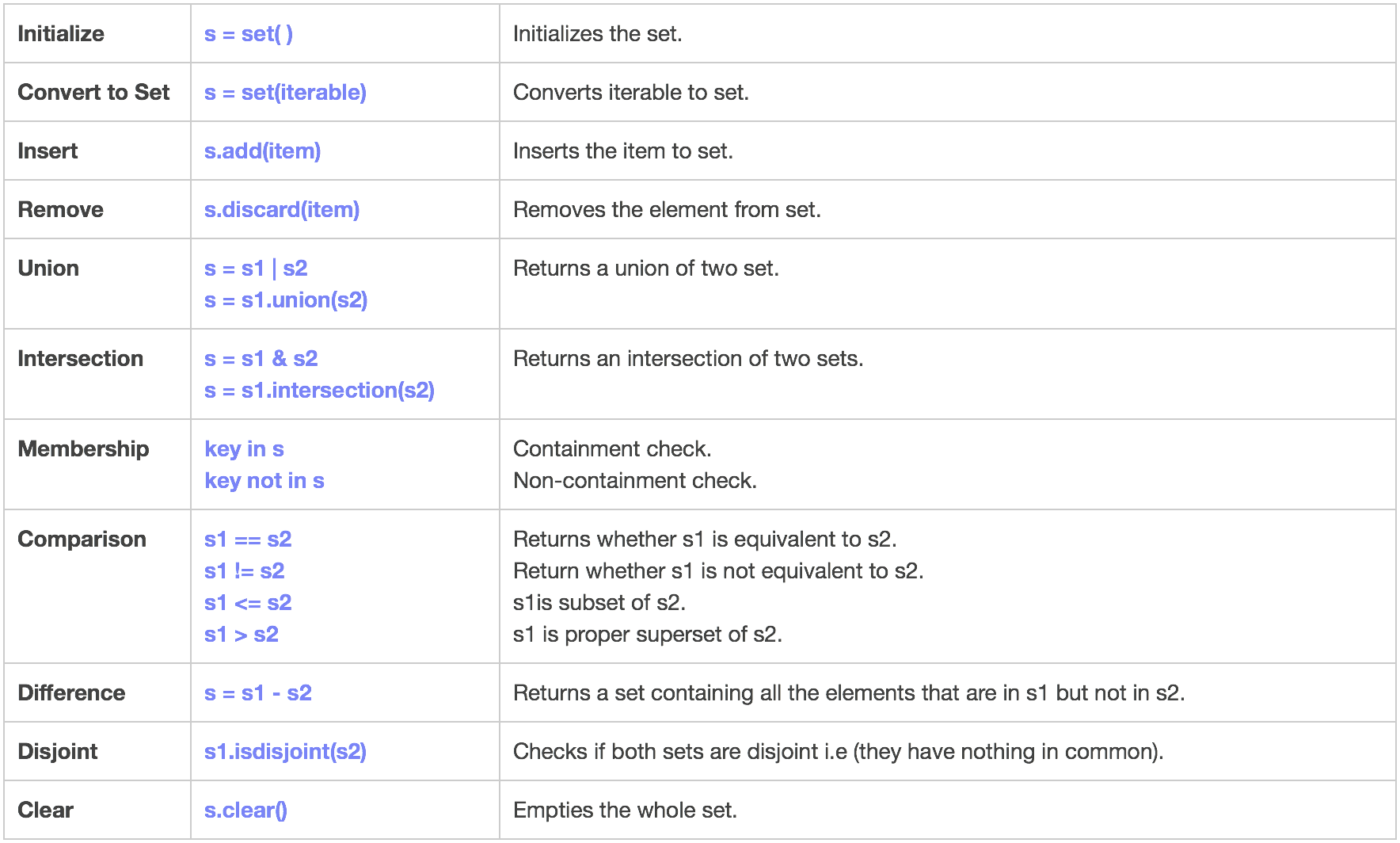
- A Set is an unordered collection data type that is iterable, mutable, and has no duplicate elements.
- Python’s set class represents the mathematical notion of a set.
- The major advantage of using a set, as opposed to a list, is that it has a highly optimized method for checking whether a specific element is contained in the set.
- This is based on a data structure known as a hash table.
- Frozen sets are immutable objects that only support methods and operators that produce a result without affecting the frozen set or sets to which they are applied.
- However there are two major pitfalls in Python sets:
- The set doesn’t maintain elements in any particular order.
- Only instances of immutable types can be added to a Python set.
Implementation:
# set(): initilaize
set1 = set()
# set(): convert to set
set2 = set([3, 4, 5, 3, 6, 5, 7, 5, 8])
# add(): Insert in set
for i in range(1, 6):
set1.add(i)
print("Set1 = {}\nSet2 = {}".format(set1, set2))
# discard(): Remove 8 from set2
set2.discard(8)
print("Set2 after 8 is removed = {}\n".format(set2))
# union(): Union of set1 and set2
set3 = set1 | set2 # set1.union(set2)
print("Union of Set1 & Set2: Set3 = {}".format(set3))
# intersection(): Intersection of set1 and set2
set4 = set1 & set2 # set1.intersection(set2)
print("Intersection of Set1 & Set2: Set4 = {}\n".format(set4))
# in : check membership
print("Is 7 present in set1 ? : {}".format(7 in set1))
print("Is 7 present in set2 ? : {}\n".format(7 in set2))
# Comparison Operators
# Checking relation between set3 and set4
if set3 > set4: # set3.issuperset(set4)
print("Set3 is superset of Set4.")
elif set3 < set4: # set3.issubset(set4)
print("Set3 is subset of Set4.")
else : # set3 == set4
print("Set3 is same as Set4.")
# displaying relation between set4 and set3
if set4 < set3: # set4.issubset(set3)
print("Set4 is subset of Set3.\n")
# difference: between set3 and set4
set5 = set3 - set4
print("Elements in Set3 and not in Set4: Set5 = {}.".format(set5))
# isdisjoint(): Check if set4 and set5 are disjoint sets
if set4.isdisjoint(set5):
print("Set4 and Set5 have nothing in common.")
# clear(): Remove all the values of set5
set5.clear()
print("After applying clear on set5 now set5 = {}.".format(set5))
Output:

Stack

Implementation
# import
from queue import LifoQueue
# Initilaize
s = LifoQueue(maxsize=5)
# put(): to psuh data to stack
print("Push 5, 9, 1, 7 to stack.")
s.put(5) ; s.put(9); s.put(1); s.put(7)
# get(): to pop data from stack
print("Data popped from stack : {}".format(s.get()))
# queue[-1]: top of the stack
print("Data at top of stack : {}".format(s.queue[-1]))
# qsize(): Size of stack
print("Size of stack : {}".format(s.qsize()))
# full(): Check full
print("Is full? : {}".format(s.full()))
# empty(): Check empty
print("Is empty? : {}".format(s.empty()))
Output:

Queue

Implementation
# import
from queue import Queue
# Initilaize
q = Queue(maxsize=5)
# put(): to enqueue data to queue
print("Enqueue 5, 9, 1, 7 to queue.")
q.put(5) ; q.put(9); q.put(1); q.put(7)
# get(): to dequeue data from queue
print("Data dequeued from queue : {}".format(q.get()))
# queue[0]: front of the queue
print("Data at front of queue : {}".format(q.queue[0]))
# queue[-1]: rear of the queue
print("Data at rear of queue : {}".format(q.queue[-1]))
# qsize(): Size of queue
print("Size of queue : {}".format(q.qsize()))
# full(): Check full
print("Is full? : {}".format(q.full()))
# empty(): Check empty
print("Is empty? : {}".format(q.empty()))
Output:

3. Deque
A double-ended queue is an abstract data type that generalizes a queue.
Here, elements can be added to or removed from either the front or back.
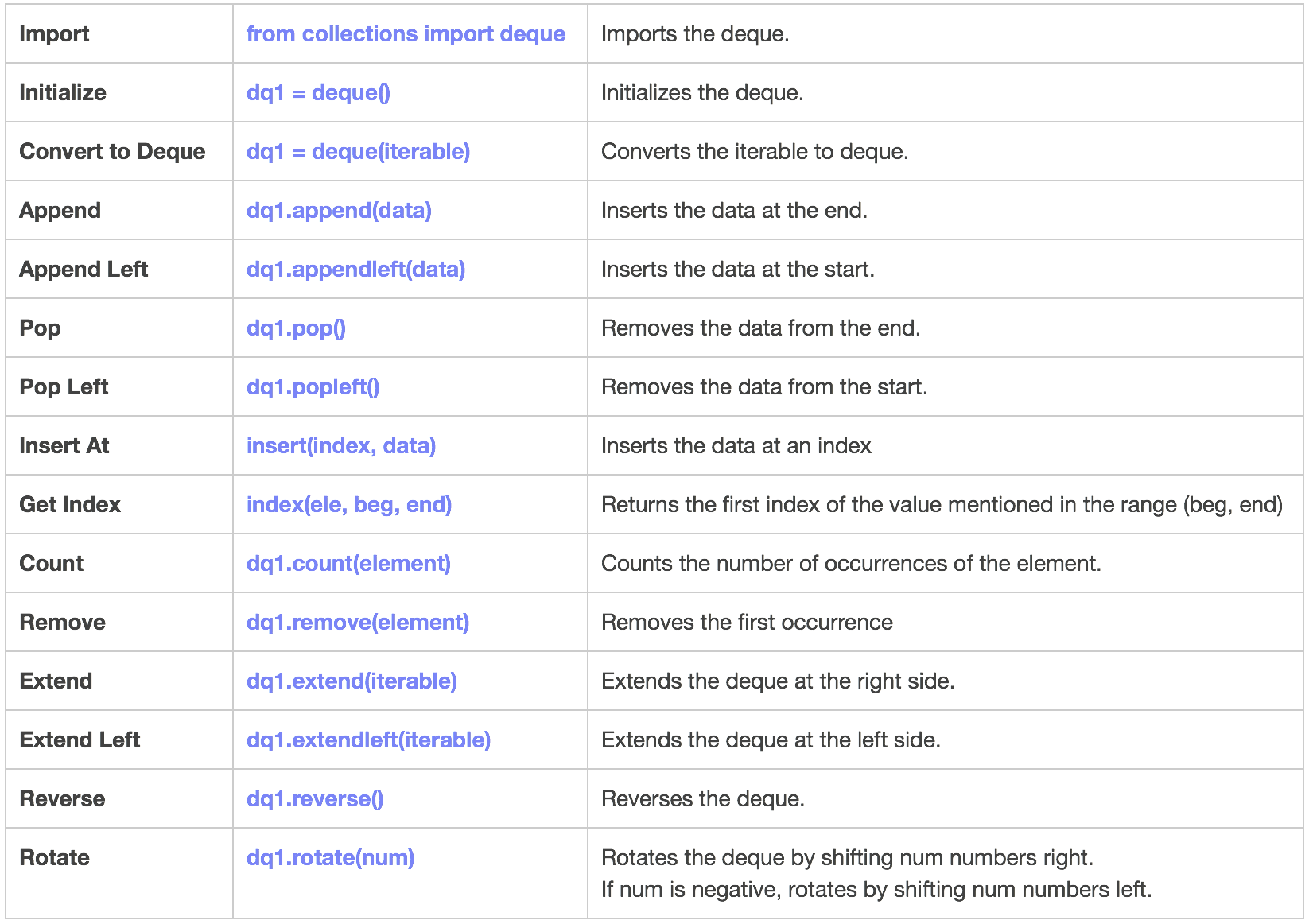
Implementation
# import
from collections import deque
# initialize
dq = deque([1,2,3])
print ("Current Deque: {}".format(dq))
# append(): Insert 4 at end
dq.append(4)
print ("Deque after append 4 at right is: {}".format(dq))
# append(): Insert 6 at start
dq.appendleft(6)
print ("Deque after append 6 at left is: {}".format(dq))
# pop(): Pop from end
dq.pop()
print ("Deque after pop from right is : {}".format(dq))
# popleft(): Pop from start
dq.popleft()
print ("Deque after pop from left is : {}".format(dq))
#================================================================
dq = deque([1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 2, 4])
print ("\nNew Current Deque : {}".format(dq))
# insert(): Insert 7 at 5th position
dq.insert(4, 7)
print ("Deque after insert 7 at 5th position is : {}".format(dq))
# insert(): Occurrence of 4 b/w 2nd and 7th index.
print ("In Deque 4 first occurs at a position : {}".format(dq.index(4, 2, 7)))
# count(): Count the occurrences of 3
print ("In Deque count of 3 : {}".format(dq.count(3)))
# remove(): Remove the first occurrence of 3
dq.remove(3)
print ("Deque after after Deleting first occurrence of 3 is : {}".format(dq))
#================================================================
dq = deque([1, 2, 3])
print ("\nNew Current Deque : {}".format(dq))
# extend(): To add [4, 5, 6] at right end
dq.extend([4, 5, 6])
print ("Deque after extend deque at end is : {}".format(dq))
# extendleft(): adds 7,8,9 at left end
dq.extendleft([7,8,9])
print ("Deque after extend deque start : {}".format(dq))
# rotate(): rotates by 3 to right
dq.rotate(3)
print ("Deque after rotate right by 3 : {}".format(dq))
# rotate(): rotates by 3 to left
dq.rotate(-3)
print ("Deque after rotate left by 3 : {}".format(dq))
# reverse(): reverse the deque
dq.reverse()
print ("Deque after reversed : {}".format(dq))
Output:

Heap
- Heap data structure is mainly used to represent a priority queue.
- In Python, it is available using “heapq” module.
- The property of this data structure in python is that each time the smallest of heap element is popped(min heap).
- Whenever elements are pushed or popped, heap structure in maintained.
- The heap[0] element also returns the smallest element each time.
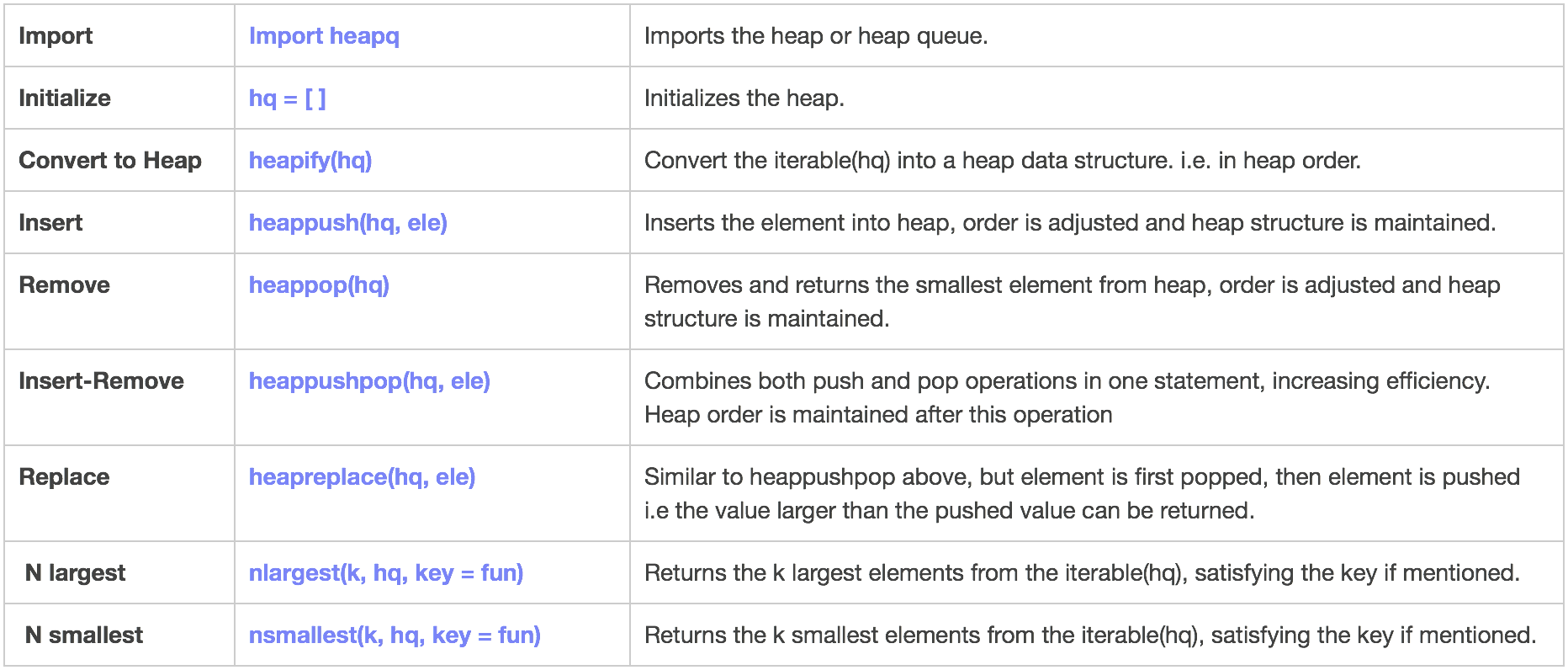
Implementation:
# import
import heapq
# a normal list
hq = [5, 7, 9, 1, 3]
# heapify(): to convert list to heap or to constrain the heap order
heapq.heapify(hq)
# Created Heap
print ("The created heap is : {}".format(hq))
# heappush(): push 4 to heap
heapq.heappush(hq, 4)
print ("Heap after 4 is pushed : {}".format(hq))
# using heappop() to pop smallest element
print ("The popped and smallest element is : {}".format(heapq.heappop(hq)))
print ("Heap after popping : {}".format(hq))
#===========================================================================
hq1 = [5, 7, 9, 4, 3]; hq2 = [5, 7, 9, 4, 3]
heapq.heapify(hq1); heapq.heapify(hq2)
print("\nTwo same newly created heaps: {}".format(hq1))
# heappushpop(): to push and pop items simultaneously pops 2
print ("The popped item from 1st using heappushpop(2) is: {}".format(heapq.heappushpop(hq1, 2)))
print("1st heap now: {}".format(hq1))
# heapreplace(): to push and pop items simultaneously pops 3
print ("The popped item from 2nd using heapreplace(2) is: {}".format(heapq.heapreplace(hq2, 2)))
print("2nd heap now: {}".format(hq2))
#===========================================================================
hq = [6, 7, 9, 4, 3, 5, 8, 10, 1]
heapq.heapify(hq)
print("\nNewly created heap: {}".format(hq))
# nlargest(): to print 3 largest numbers prints 10, 9 and 8
print("The 3 largest numbers in list are : {}".format(heapq.nlargest(3, hq)))
# nsmallest(): to print 3 smallest numbers prints 1, 3 and 4
print("The 3 smallest numbers in list are : {}".format(heapq.nsmallest(3, hq)))
Output:
