Multi-threading in Java
Multi-tasking
- Multitasking is a process of executing multiple tasks simultaneously.
- We use multitasking to utilize the CPU.
- Multitasking can be achieved in two ways:
- Process-based Multi-tasking (Multi-processing)
- Each process has an address in memory, in other words, each process allocates a separate memory area.
- A process is heavyweight.
- Cost of communication between the process is high.
- Switching from one process to another requires some time for saving and loading registers, memory maps, updating lists, etc.
- Thread-based Multi-tasking (Multi-threading)
- Threads share the same address space.
- A thread is lightweight.
- Cost of communication between the thread is low.
- Process-based Multi-tasking (Multi-processing)
What is Multi-threading ?
- Multithreading is a feature that allows concurrent execution of two or more parts of a program for maximum utilization of CPU.
- Each part of such program is called a thread.
- So, threads are light-weight processes within a process.
What are threads ?
- A thread is a lightweight subprocess, the smallest unit of processing.
- It has a separate path of execution.
- Threads are independent, if there occurs exception in one thread, it doesn’t affect other threads.
- It uses a shared memory area.
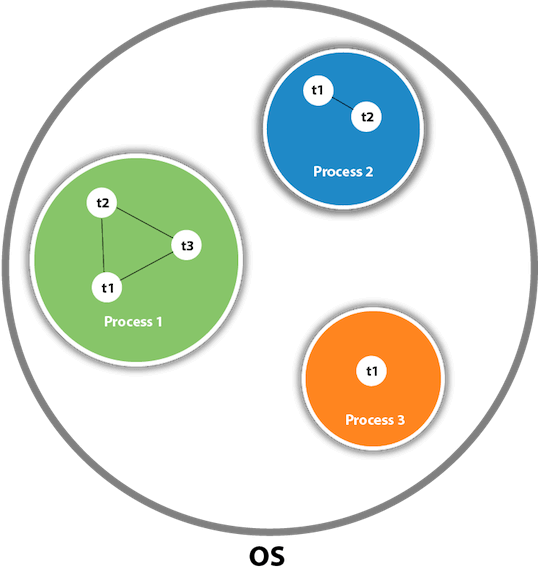
[Note :** There can be multiple processes inside the OS, and one process can have multiple threads.
How to create threads ?
Threads can be created by using two mechanisms :
- Extending the Thread class
- Implementing the Runnable Interface
1. Extending the Thread Class
- We create a class that extends the java.lang.Thread class.
- This class overrides the run() method available in the Thread class.
- A thread begins its life inside run() method.
- We create an object of our new class and call start() method to start the execution of a thread.
- Start() invokes the run() method on the Thread object.
// Java code for thread creation by extending the Thread class
class MultithreadingDemo extends Thread {
public void run() {
try {
// Displaying the thread that is running
System.out.println ("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " is running");
}
catch (Exception e) {
// Throwing an exception
System.out.println ("Exception is caught");
}
}
}
// Main Class
public class Multithread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 8; // Number of threads
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
MultithreadingDemo object = new MultithreadingDemo();
object.start();
}
}
}
Output:
Thread 8 is running
Thread 9 is running
Thread 10 is running
Thread 11 is running
Thread 12 is running
Thread 13 is running
Thread 14 is running
Thread 15 is running
2. Implementing the Runnable Interface
- We create a new class which implements java.lang.Runnable interface and override run() method.
- Then we instantiate a Thread object and call start() method on this object.
// Java code for thread creation by implementing the Runnable Interface
class MultithreadingDemo implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
// Displaying the thread that is running
System.out.println ("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + " is running");
}
catch (Exception e) {
// Throwing an exception
System.out.println ("Exception is caught");
}
}
}
// Main Class
class Multithread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 8; // Number of threads
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
Thread object = new Thread(new MultithreadingDemo());
object.start();
}
}
}
Output:
Thread 8 is running
Thread 9 is running
Thread 10 is running
Thread 11 is running
Thread 12 is running
Thread 13 is running
Thread 14 is running
Thread 15 is running
Thread Class vs. Runnable Interface
-
If we extend the Thread class, our class cannot extend any other class because Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance. But, if we implement the Runnable interface, our class can still extend other base classes.
-
We can achieve basic functionality of a thread by extending Thread class because it provides some inbuilt methods like yield(), interrupt() etc. that are not available in Runnable interface.