Miscellaneous Coding Patterns Problems
Here are some interesting list of miscellaneous problems.
1. Trapping Rain Water Problem
Problem:
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
Example:
Input: [0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
Output: 6
Approach-1: Calculate Right pole and Left pole in Advance
- Find left_pole and right_pol array for every element similar to finding leader in array.
- Then iterate over every element and find the water contributed by that particular element by min(left_pole[i], right_pole[i]) - arr[i].
Implementation
Code:
def trap(height):
n = len(height)
right_pole = [0]*n
right_pole[n-1] = height[n-1]
for i in range(n-2, -1, -1):
right_pole[i] = max(right_pole[i+1], height[i])
left_pole = [0]*n
left_pole[0] = height[0]
for i in range(1, n):
left_pole[i] = max(left_pole[i-1], height[i])
water = 0
for i in range(n):
water += min(left_pole[i], right_pole[i]) - height[i]
return water
Complexity:
- Time: O(n)
- Auxilliary Space: O(n)
Approach-2: Use two pointer to track Left pole and Right pol
- Try to eliminate calculating left_pole and right_pole.
- Try doing in the one iteration only.
Implementation:
Code:
def trap2(height):
n = len(height)
i = 0
j = n-1
left_max = 0
right_max = 0
water = 0
while(i < j):
if(height[i] < height[j]):
left_max = max(left_max, height[i])
water += left_max - height[i]
i += 1
else:
right_max = max(right_max, height[j])
water += right_max - height[j]
j -= 1
return water
Complexity:
- Time: O(n)
- Auxilliary Space: O(1)
2. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree
Serialization & Deserialization
It is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed (deserialized) later in the same or another computer environment.
Problem:
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
Approach: Use DFS on Binary Tree
A simple solution is to store both Inorder and Preorder traversals. This solution requires requires space twice the size of Binary Tree. We can save space by storing Preorder traversal and a marker for NULL pointers.
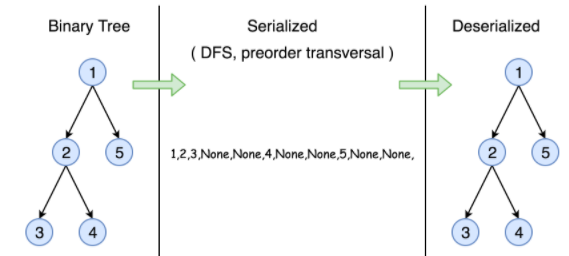
Other Examples:

Implementation:
Code:
class TreeNode(object):
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
serialized_btree = []
self._modified_pre_order(root, serialized_btree)
return ",".join(serialized_btree)
def _modified_pre_order(self, root, serialized_btree):
if root:
serialized_btree.append(str(root.val))
self._modified_pre_order(root.left, serialized_btree)
self._modified_pre_order(root.right, serialized_btree)
else:
serialized_btree.append("#")
def deserialize(self, data):
nodes_list = data.split(",")
nodes_list.reverse()
return self._build_tree(nodes_list)
def _build_tree(self, nodes_list):
if not nodes_list:
return
key = nodes_list.pop()
if key != "#":
root = TreeNode(int(key))
root.left = self._build_tree(nodes_list)
root.right = self._build_tree(nodes_list)
return root
def print_tree(root):
if root:
print(root.val, end=" ")
print_tree(root.left)
print_tree(root.right)
# Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
# 1
# / \
# 2 3
# / \
# 4 5
# / \
# 7 6
root = TreeNode(1)
root.left = TreeNode(2)
root.right = TreeNode(3)
root.right.left = TreeNode(4)
root.right.right = TreeNode(5)
root.right.left.left = TreeNode(7)
root.right.left.right = TreeNode(6)
codec = Codec()
print_tree(codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root)))
print()
# 20
# /
# 8
# / \
# 4 12
# / \
# 10 14
root = TreeNode(20)
root.left = TreeNode(8)
root.left.left = TreeNode(4)
root.left.right = TreeNode(12)
root.left.right.left = TreeNode(10)
root.left.right.right = TreeNode(14)
codec = Codec()
print_tree(codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root)))
print()
Output:
1 2 3 4 7 6 5
20 8 4 12 10 14
Complexity:
- Time complexity: O(N) : In both serialization and deserialization functions, we visit each node exactly once, thus the time complexity is O(N), where N is the number of nodes, i.e. the size of tree.
- Space complexity: O(N) : In both serialization and deserialization functions, we keep the entire tree, either at the beginning or at the end, therefore, the space complexity is O(N).